
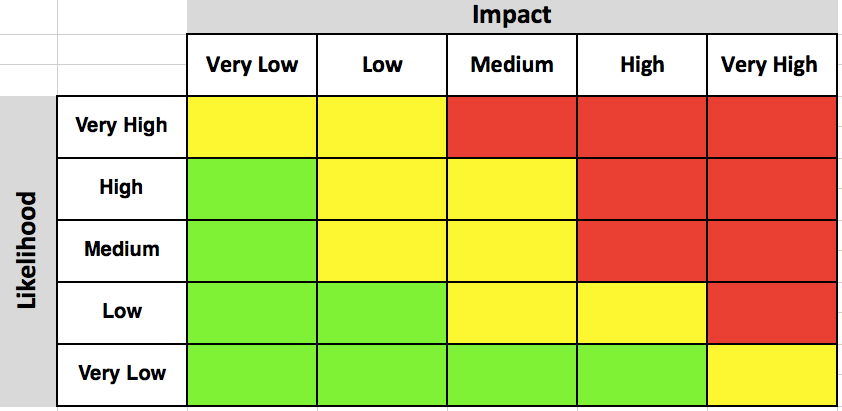
- Risk probability chart manual#
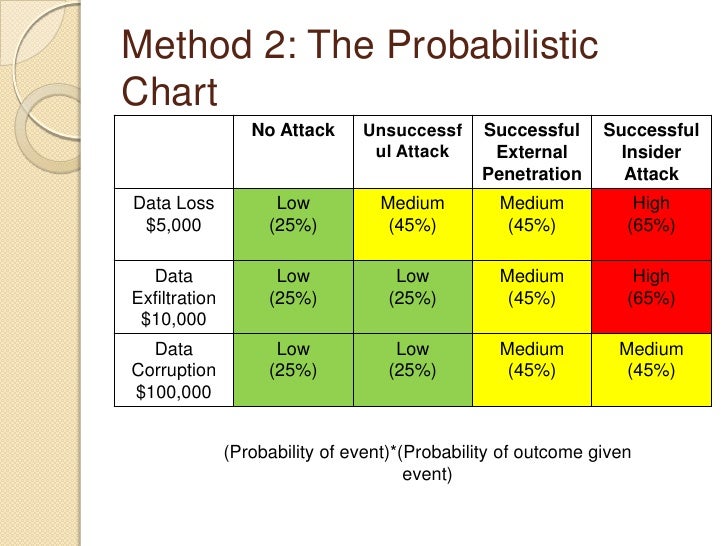
- Risk probability chart plus#
- Risk probability chart series#
Risk probability chart manual#
Project management Project management covers planning, milestones, objectives, scope, control, estimating, assumptions and constraints, problem statements, mission statements, identifying strategy, deliverables, work breakdown structure (wbs), plan types, dependencies, PERT, critical path management (cpm), cost terminology, the project manager, report writing, manual methods, resource levelling, popular project management systems, quality function deployment and more. Also, Product-based planning, change control technique and quality review technique and more. The components – Business case, Management of risk, Quality in a project environment, Configuration management Change control, Organisation, Plans and Controls. PRINCE2 2005 PRINCE2 2005 covers definition, terminology, the processes - Starting up a Project (SU), Initiating a Project (IP), Directing a Project (DP), Controlling a Stage (CS), Managing Product Delivery (MP), Managing Stage Boundaries (SB), Closing a Project (CP) and Planning (PL). The processes – starting up a project, directing a project, initiating a project, controlling a stage, managing product delivery, managing a stage boundary, closing a project and tailoring PRINCE2 2009 and more. PRINCE2 2009 PRINCE2 2009 updates PRINCE2 2005 and covers the principles, the themes - business case, organisation, quality, plans, risk, change and progress. Whilst this may constitute an unsatisfactory situation the board may decide to accept the risk.Įlsewhere summaries some of the considerations when modifying a plan. On the other hand, the analysis may indicate a 35% likelihood of meeting the project end date. This will involve dependencies, proactive aspects in the plan to mitigate risks and attention to any contingency plans. If the analysis shows that there is only a 10% chance of meeting the completion date you will need to review the plan. Key conditions and assumptions should be mentioned.įrom this simplified view of the overall risk to the project you may derive knowledge on the project end date which is unacceptable. The information can be presented against data in the base plan (or reference plan), for example, the project end date thus demonstrating the affect of delays. The larger the gap the more significant the ‘S’ curve to the right. The ‘gap’ between the ‘S’ curves on the ‘x’ axis (delay, cost etc) will give some indication of relative importance. If there are several low risks that are not significant in their own right combine these first and present this as one of the ‘S’ curves in the presentation. Perhaps 5 or 6 major risk areas would be the maximum to present in this format at one time so focus on the key risk areas at a high level. 
Risk probability chart plus#
the previous total plus the latest risk).
Risk probability chart series#
In this way a series of ‘S’ curves can be generated where each one represents the total of risk to date (i.e. Other areas to consider when reviewing risk.Simple estimating of risk - more detail.Ownership - risks, responsibilities and contractors.Organise - prioritise risks and responses.What are the basic overall process steps?.What are the core process steps to assess a risk?.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
